Performance and Throttling Dialog
To configure bandwidth:
Define this to control the amount of traffic going out of your site.
When defined, this is the maximum bandwidth that Zerto uses from this site to all peer recovery sites.
Zerto throttles the bandwidth used so that on average, bandwidth usage from the protected site does not exceed the limit.
If you do not specify bandwidth throttling, the default is for Zerto to automatically assign the bandwidth used per VPG, based on using the maximum available and then prioritizing the usage according to the priority set for the VPGs sending data over the WAN.
|
•
|
When you select Bandwidth Throttling, by default, Limited is selected. |
|
•
|
In the text area that become available, set the MB/sec. The valid range is from 0 to 1300 MB/sec. |
|
•
|
With 0 MB/sec, Zerto automatically assigns the bandwidth used per VPG, based on using the maximum available and then prioritizing the usage according to the priority set for the VPGs sending data over the WAN. |
|
•
|
Enter the MB/sec when the value required is 100 MB/sec or more. |
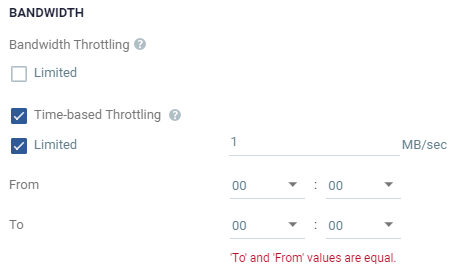
Define this to throttle the bandwidth during specific times. For example, during the daily peak transaction period you can change the bandwidth throttling, to override the general setting.
|
•
|
Limited: Select to define the limit, then define: |
|
•
|
From: The hour and the minute to start the throttling, using a 24-hour clock. |
|
•
|
To: The hour and the minute to end the throttling, using a 24-hour clock. |
|
•
|
Click Show advanced settings... |
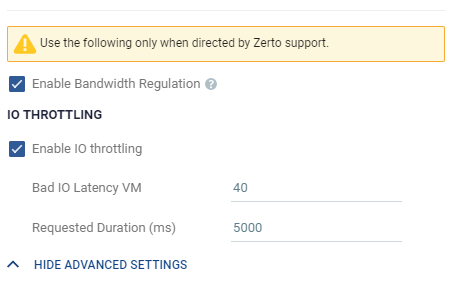
Important:
Advanced settings must only be changed in coordination with Zerto support.
|
•
|
Enable Bandwidth Regulation: Use this for troubleshooting - to enable regulating the bandwidth. |
|
•
|
Enable IO throttling: If a host is handling too many IOs, then the IOs begin to get high latencies. To offset this the VRA sends fewer concurrent IOs. The latency is measured by taking the average latency for all IOs over a set period of time. For example, when the period is 5000 milliseconds and the bad IO latency is 40, the average latency is calculated every 5 seconds, and if the average latency exceeds 40, the VRA sends fewer concurrent IOs. |
|
•
|
Bad IO Latency VM: The threshold above which the latency is considered high, and therefore bad. |
|
•
|
Requested Duration (ms): The period of time used to measure the average latency. |